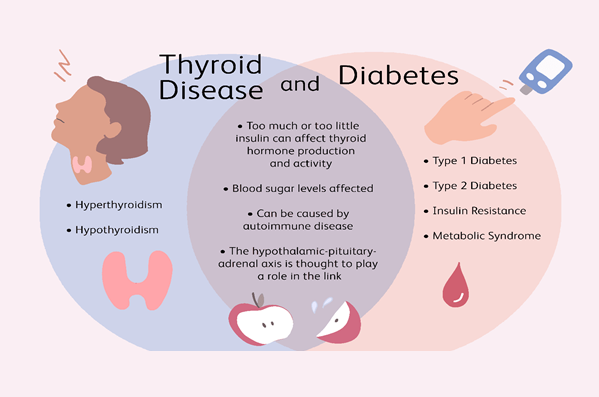
Thyroid disease and diabetes are the two most prevalent endocrine disorders, and it has been documented that there is increased prevalence of thyroid disorders in patients with diabetes mellitus and vice versa.
They are related to each other. Thyroid has an impact on glucose control, and an adverse influence on diabetes management in patients.

The thyroid gland is responsible for everyday body activities that also includes metabolism. Thyroid gland abnormalities may disrupt the metabolic function in body, leading to accumulation of blood sugar (glucose) in the blood, rather than being used for energy production. This increases your risk of developing diabetes and makes it more difficult to control your blood sugar levels if you already have diabetes.
Hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid) and Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) are closely connected.
In hyperthyroidism, metabolism increases, insulin is removed faster from the body than usual and leads to increased blood sugar levels and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Thyroid-related hyperglycemia also contributes to metabolic syndrome with symptoms like high blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, high triglyceride levels, low HDL cholesterol, and obesity and there is an increased insulin resistance which causes poor diabetic control or worsens the condition of patient, leading to increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Thyroid dysfunction also has its effect on insulin production. Insulin works in the body to allow cells to use glucose as a source of energy. This helps to reduce the blood sugar levels.
Hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid), slows down the metabolism. Hence, insulin levels remain increased, causing blood sugar levels to decrease (Hypoglycemia). This decrease in diabetic patients can be severe, resulting in dizziness, disorientation, and unconsciousness and sometimes may lead to coma.
So there is a strong relationship existing between thyroid diseases and diabetes mellitus. It also shows that the thyroid hormones play a role in controlling glucose metabolism and pancreatic function, while diabetes can alter thyroid function.
If a person diagnosed with diabetes or thyroid disease, proper medical management and maintaining ideal weight with physical exercise may reduce the risk of developing the other conditions.
 Medinexus, an app dealing with childhood obesity launched
Medinexus, an app dealing with childhood obesity launched
 Conference on Diabetes
Conference on Diabetes
 Navigating Hyperthyroidism from diagnosis to care
Navigating Hyperthyroidism from diagnosis to care
Copyright @2022 Dr Suresh Damodharan. Designed and Maintained by ITindustries.com