Managing diabetes is a continuing process of expediting the knowledge, talent, and ability needed to successfully manage disease on your own. It is a particular care for all people with diabetes and has been shown to improve patient outcomes.
There are a few key self-care activities that predict positive results for diabetic patients. Healthy nutrition, physical activity, and monitoring of blood glucose, medication compliance, problem-solving abilities, risk-reduction habits and healthy coping skills.
These activities are linked to better glycemic management, fewer problems, and a higher quality of life. Furthermore, self-care covers not only the performance of these actions but also their interrelationships.
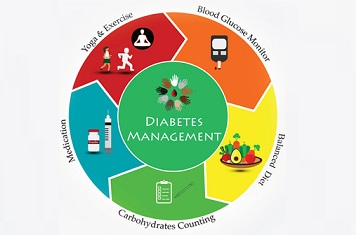
Self care monitoring - Self care monitoring offers information on present glycemic status, allowing for therapy evaluation and guiding dietary, exercise, and medication adjustments to optimise glycemic control.
Self monitoring blood glucose is recommended at least four times per day if you are on insulin and have poor glycemic control or recurrent hypoglycemia. This includes fasting, before lunch, before dinner, and before bedtime. To avoid numerous pricks per day, each value must be recorded across at least three days.
Ingest - Follow a diet plan, avoid high-fat meals and sugary foods, limit carbohydrate and have balanced nutrition food.
Sugar-sweetened foods such as fruit juice, aerated beverages, and sugar syrups should be avoided at all costs. This keeps healthy, active and controlled glucose levels.
Exercise - Should be physically active on a regular basis. Regular physical exercise and yoga, regardless of weight loss, has been linked to better health outcomes in diabetes. A total of 60 minutes of physical exercise every day, divided between aerobic activity, work-related activity, and muscle-strengthening activity, would be optimal.
Intensity and type of physical activity should be adapted to a person's ability and fitness level. If you are with co-existing cardiac disease or a history of hypoglycemia should be treated with caution.
Medication - The patient-doctor relationship's quality is frequently a deciding factor. It's essential to continue the treatment plan as prescribed and to discuss any concerns you have about diabetes treatment with your doctor, who can change the plan to ensure that your goals are fulfilled and no complications arise.
Multiple demographic, socioeconomic, and social support characteristics can all be regarded as beneficial contributors to diabetic patients' ability to self-care.
 Medinexus, an app dealing with childhood obesity launched
Medinexus, an app dealing with childhood obesity launched
 Conference on Diabetes
Conference on Diabetes
 Navigating Hyperthyroidism from diagnosis to care
Navigating Hyperthyroidism from diagnosis to care
Copyright @2022 Dr Suresh Damodharan. Designed and Maintained by ITindustries.com